News trauma studied
 Researchers have identified a feedback cycle that keeps us consuming concerning news.
Researchers have identified a feedback cycle that keeps us consuming concerning news.
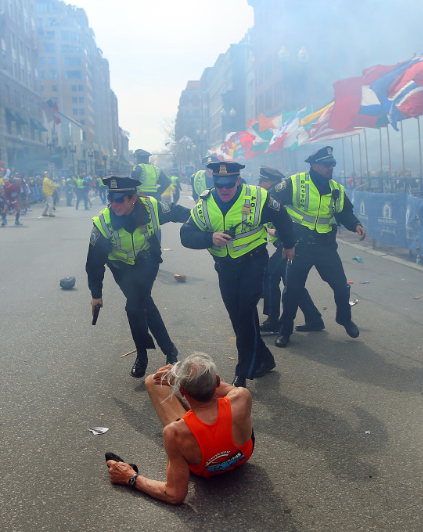
A US study has found that being exposed to media coverage of a violent event, such as a mass shooting, can lead to post-traumatic stress symptoms that make people more likely to consume media coverage of the next violent event.
Researchers analysed data collected between the 2013 Boston Marathon bombing and the 2016 Orlando Pulse nightclub shooting.
They say their report found people were traumatised following one event were more likely to tune in the next time something terrible happened.
Continued exposure to traumatic news has been linked with poor mental health in the immediate aftermath and post-traumatic stress and physical health problems over time.
“People may be turning to media coverage to cope with uncertainty and to gather information that they can use to protect themselves from perceived threats, but this behaviour may backfire if it leads to more media consumption that fuels further stress symptoms and may increase the likelihood of stress-related disorders that impact cardiovascular disease,” the researchers note.







 Print
Print